Coordinated Universal Time
Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) is based on atomic time ( International Atomic Time). It is synchronized and adjusted to stay within 0.9 seconds of Universal Time (UT1). Occasionally, a "leap second" is added to UTC in order keep it in sync with UT1 (which varies due to Earth's rotation). UTC is the time used by GPSs and is the standard reference for Time Zones around the world. For instance, Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) is set equal to UTC, while other time zones are offsets from UTC by up to ± 14 hours.
Universal Time (UT1)
Solar time is time based on Earth’s rotation relative to the Sun. Apparent solar time is that measured by direct observation of the Sun or by a sundial. Mean solar time, kept by most clocks and watches, is the solar time that would be measured by observation if the Sun traveled at a uniform apparent speed throughout the year rather than, as it actually does, at a slightly varying apparent speed that depends on the seasons.
Universal Time (UT1) is the modern time standard for mean solar time and is based on Earth's rotation on its axis. The rotation of the Earth and UT1 are monitored by the International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service (IERS)
The rotation of the Earth is gradually slowing due to the tidal acceleration of the the Moon. The length of the second was originally determined from observations of the Moon between 1750 and 1890. However, the modern mean solar day is now slightly longer due to this gradual slowdown.
While Universal Time (UT1) was originally determined by measuring Earth's rotation with respect to the Sun, it is now determined more accurately by measurements of distant quasars using long baseline interferometry.
While Universal Time (UT1) is tied directly to Earth's rotation, Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) is based an atomic timescale and adjusted to approximate Universal Time (UT1) to 0.9 seconds or less. As Earth's rotation gradually slows down, Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) must be adjusted with an occasional intercalary leap second to remain within 0.9 seconds of Universal Time (UT1).
Time Zones
A time zone is a designated area of the globe that observes a uniform standard time for legal, commercial and social purposes. It is typically chosen to approximate mean solar time for a region. Time zones tend to follow the boundaries of countries and their subdivisions instead of strictly following longitude because of commercial convenience.
Most of the time zones on land are offset from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) by a whole number of hours. For example, in North America the following time zones are observed along with their offsets from UTC.
Atlantic Standard Time (AST) = UTC - 4 hours
Eastern Standard Time (EST) = UTC - 5 hours
Central Standard Time (CST) = UTC - 6 hours
Mountain Standard Time (MST) = UTC - 7 hours
Pacific Standard Time (PST) = UTC - 8 hours
If Daylight Saving Time is in effect in a particular time zone, one hour must be ADDED to the standard time to convert it to Daylight Saving Time.
World Time Zones
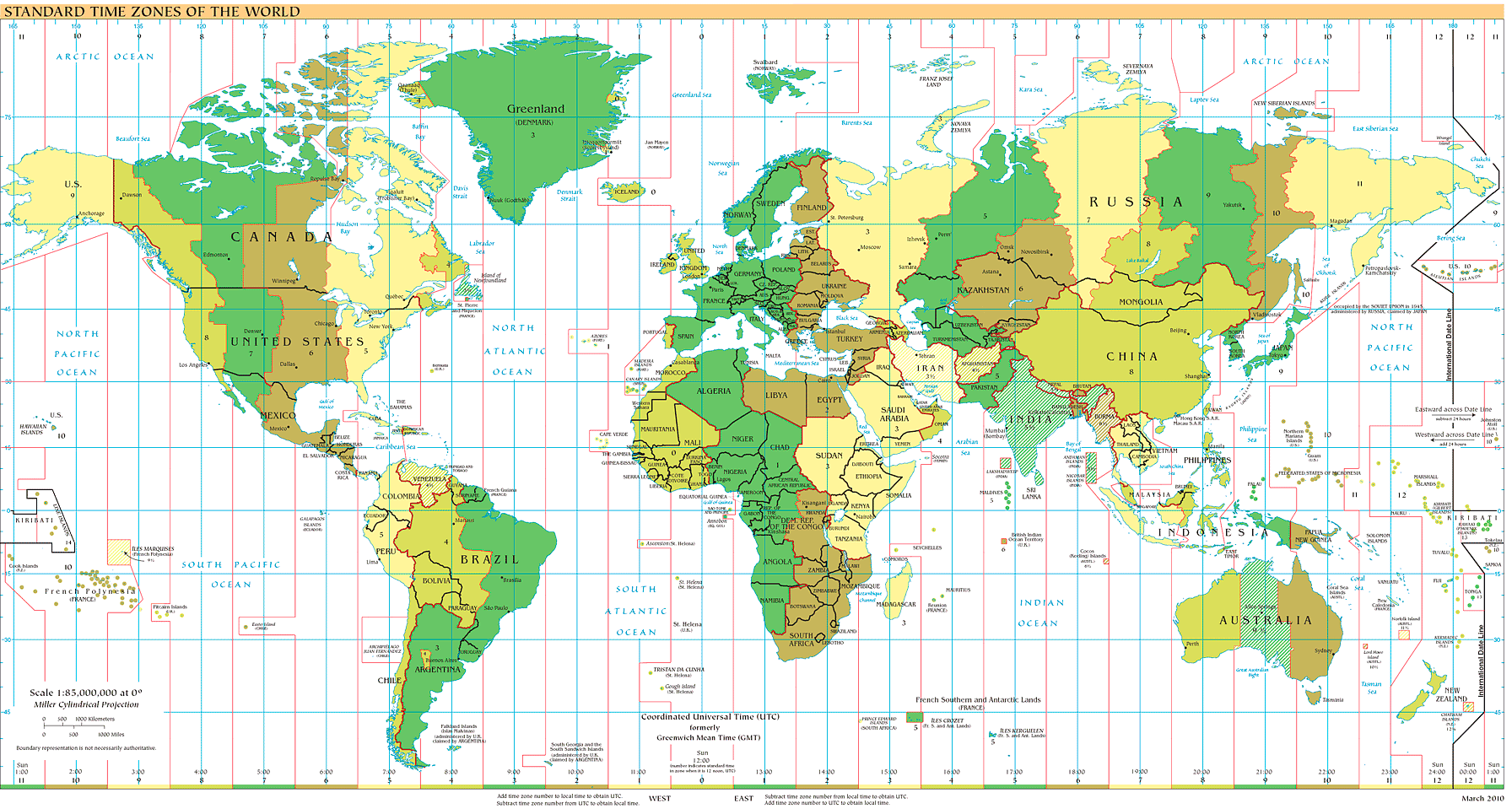
World Time Zones (click to see larger image)
Time zones for countries around the world can be determined using the map above.
For example, if you are in the Eastern Standard Time zone, you will see that your local time is 5 hours earlier than UT. In order to convert any eclipse predictions from UT to local time (i.e. - EST), you must subtract 5 hours from UT:
Local Time = UT - 5 hours
Time Zone Links
For more information on time reckoning and time zones, visit the following sites:
- A Walk Through Time - National Institute of Standards and Technology
- Systems of Time - R. E. Schmidt, U.S. Naval Observatory
- What is a Leap Second? - R. E. Schmidt, U.S. Naval Observatory
- Precise Time - Naval Oceanography Portal
- Time Zones - Wikipedia
- U.S. Time Zone - Wikipedia
- Local Times Around the World - dateandtime.com
- World Time Zones - worldtimezone.com
