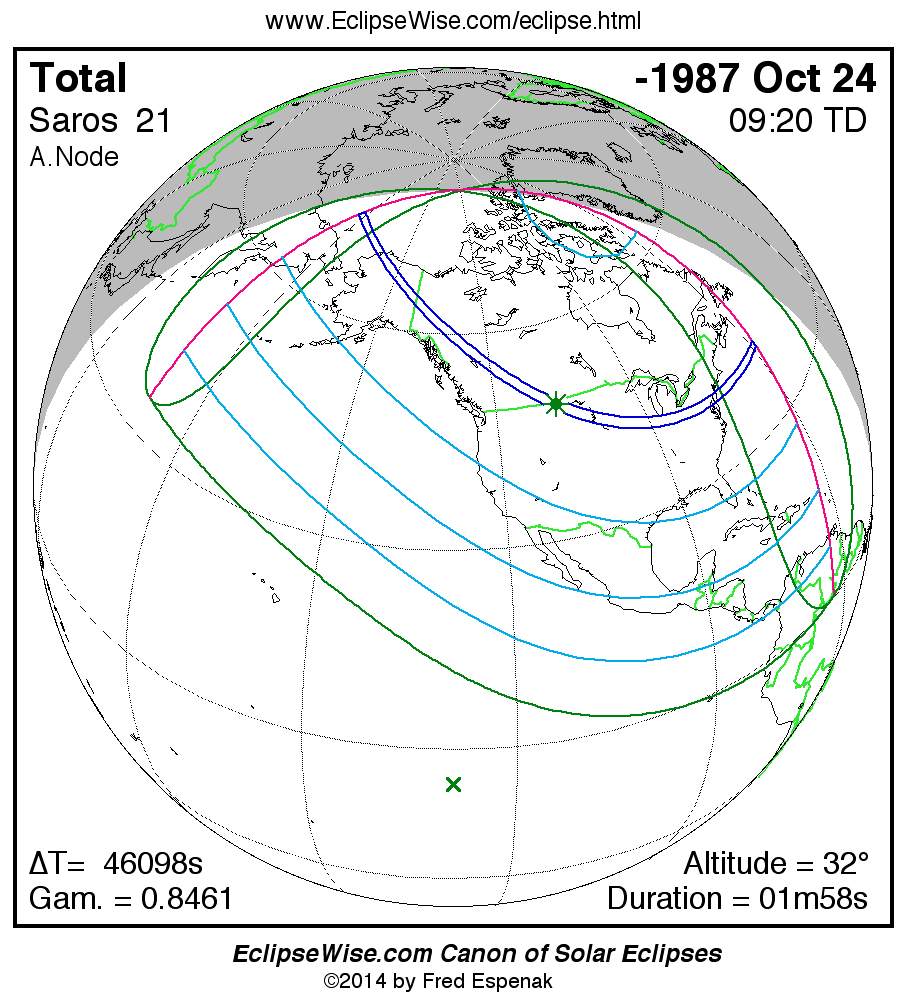
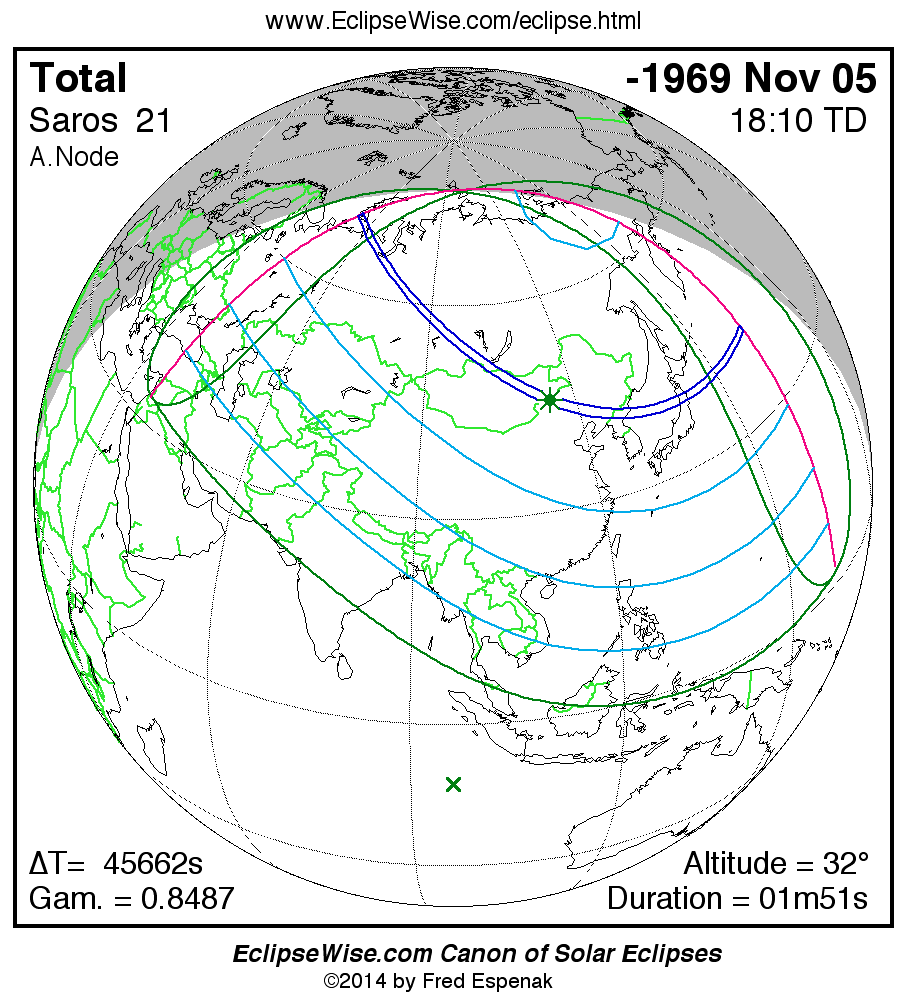
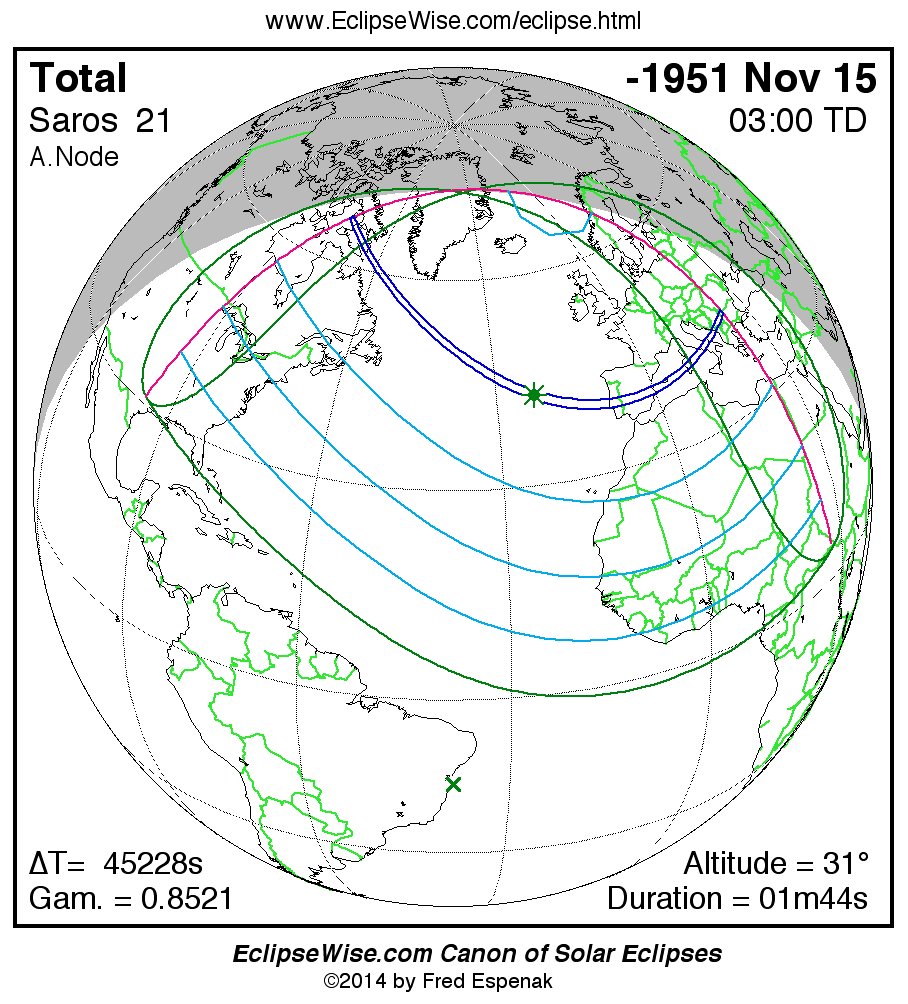
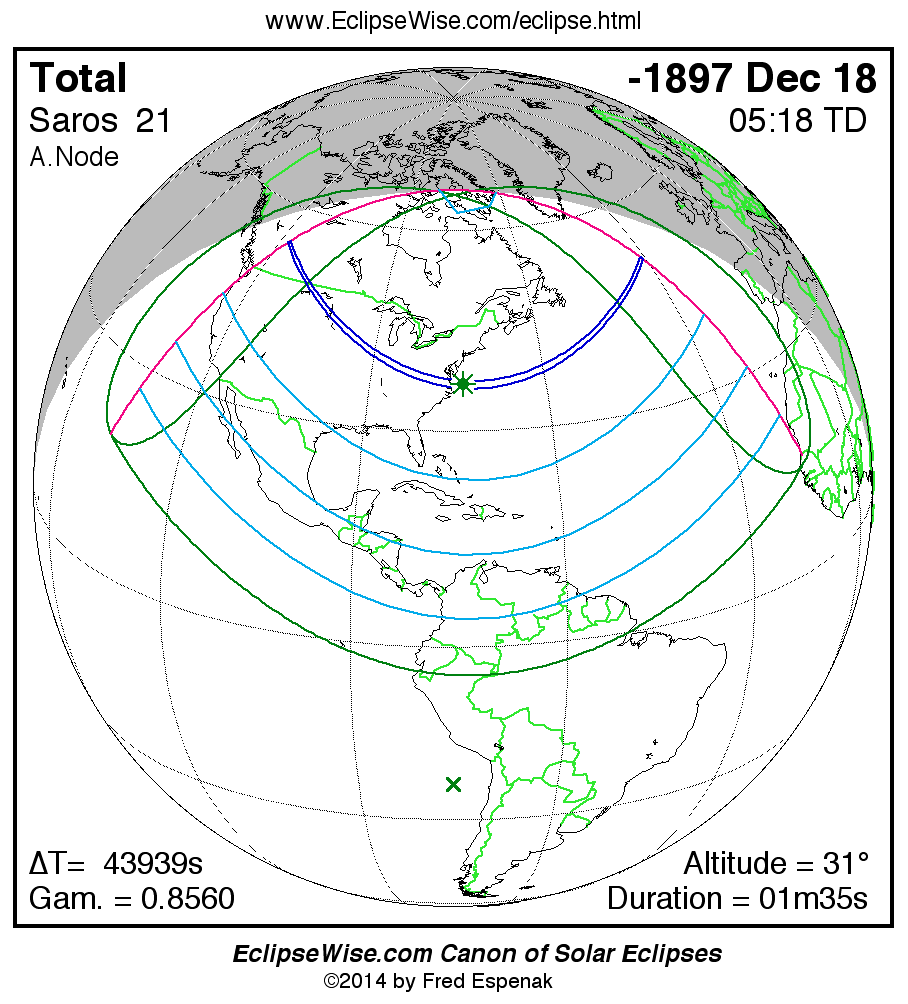
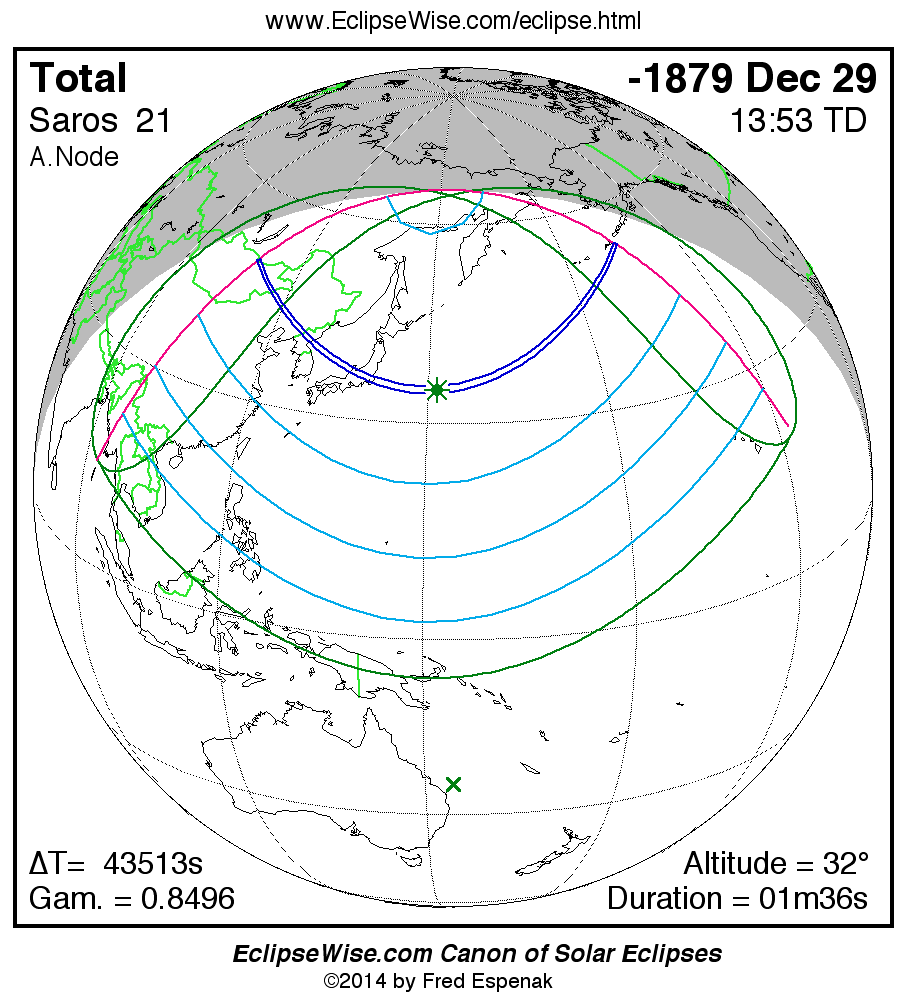
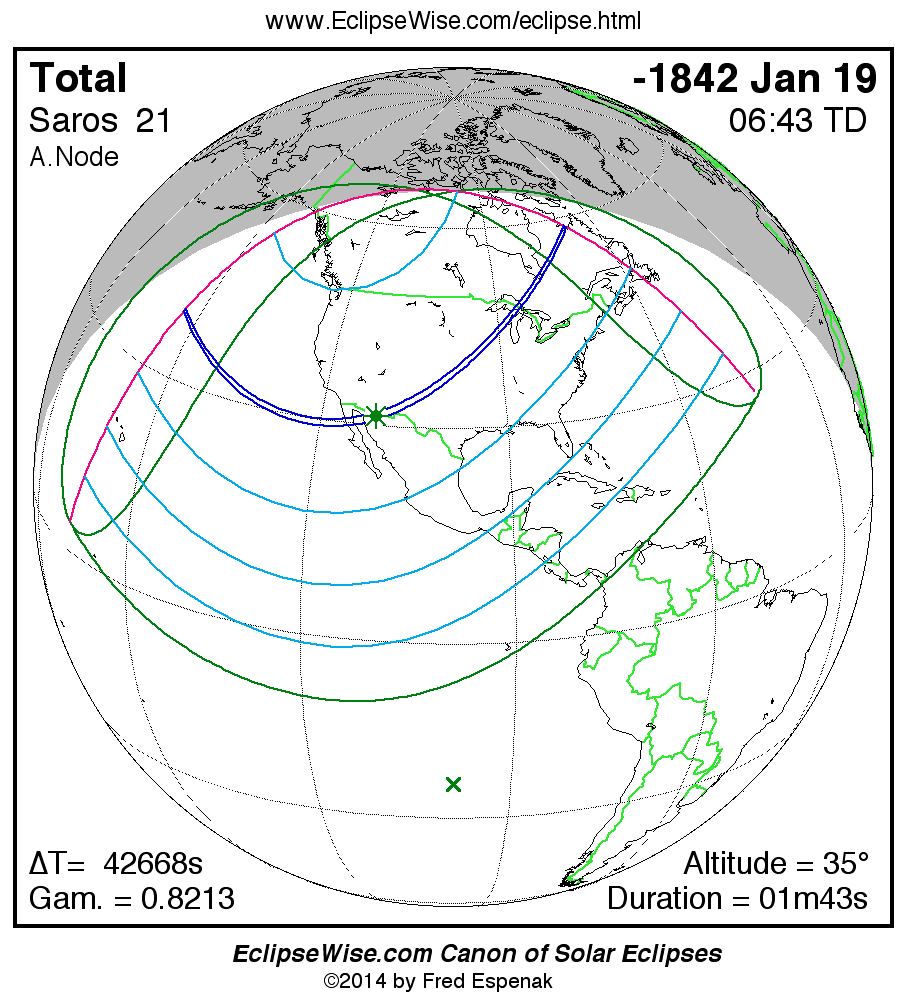
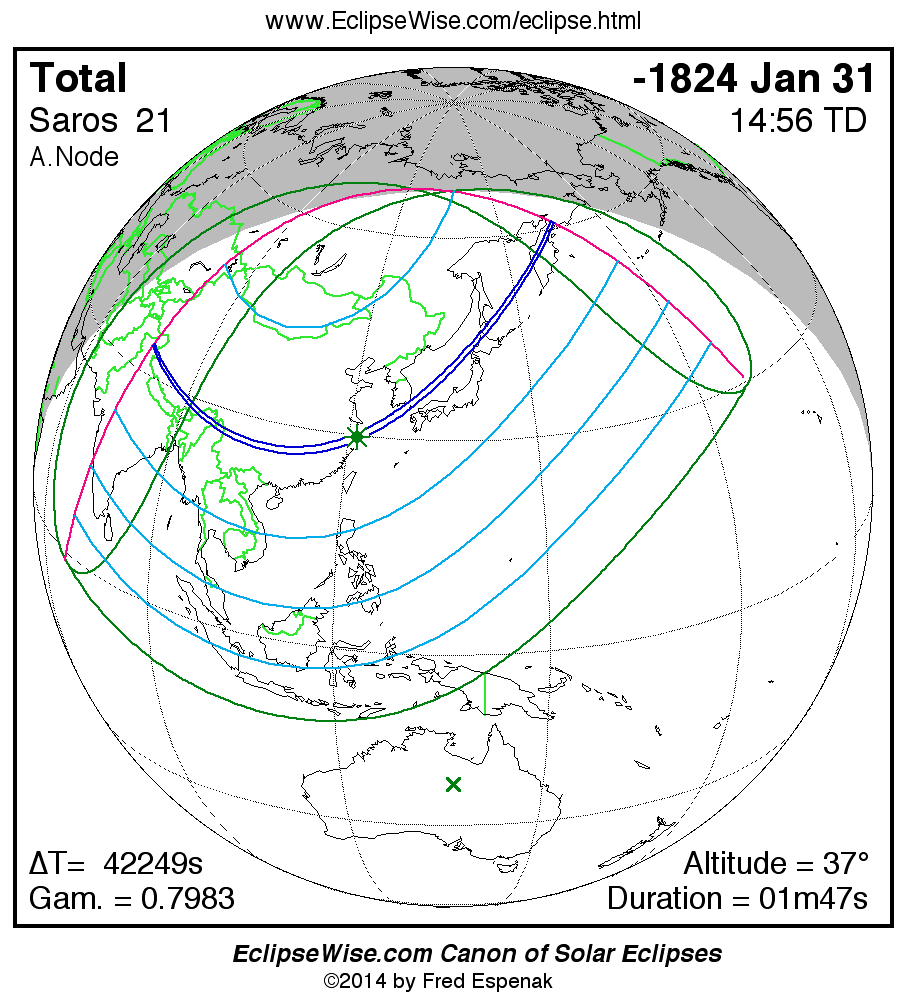
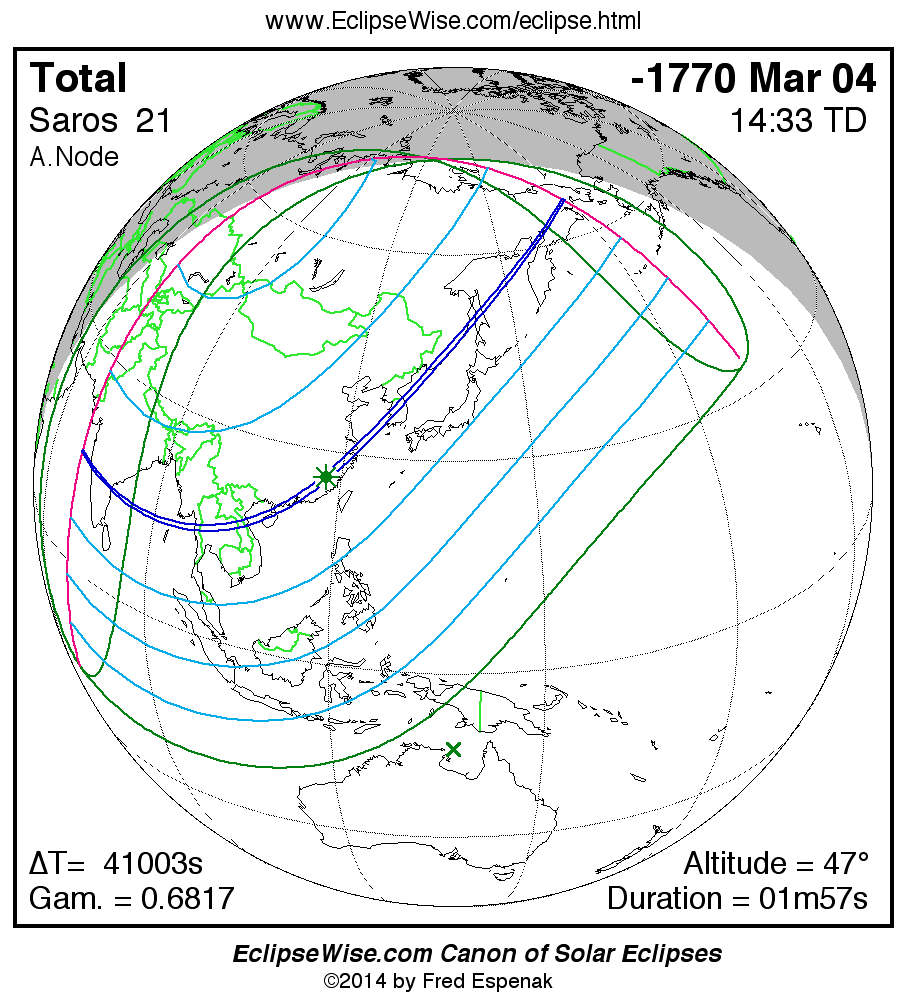
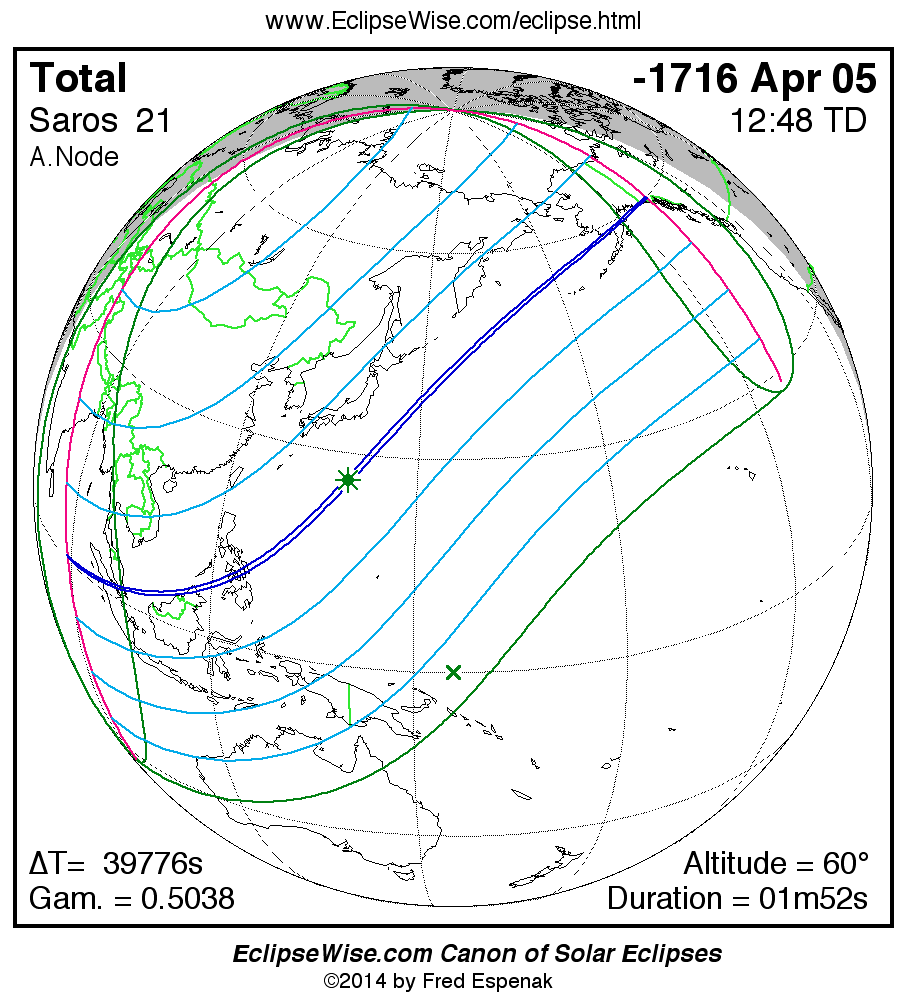
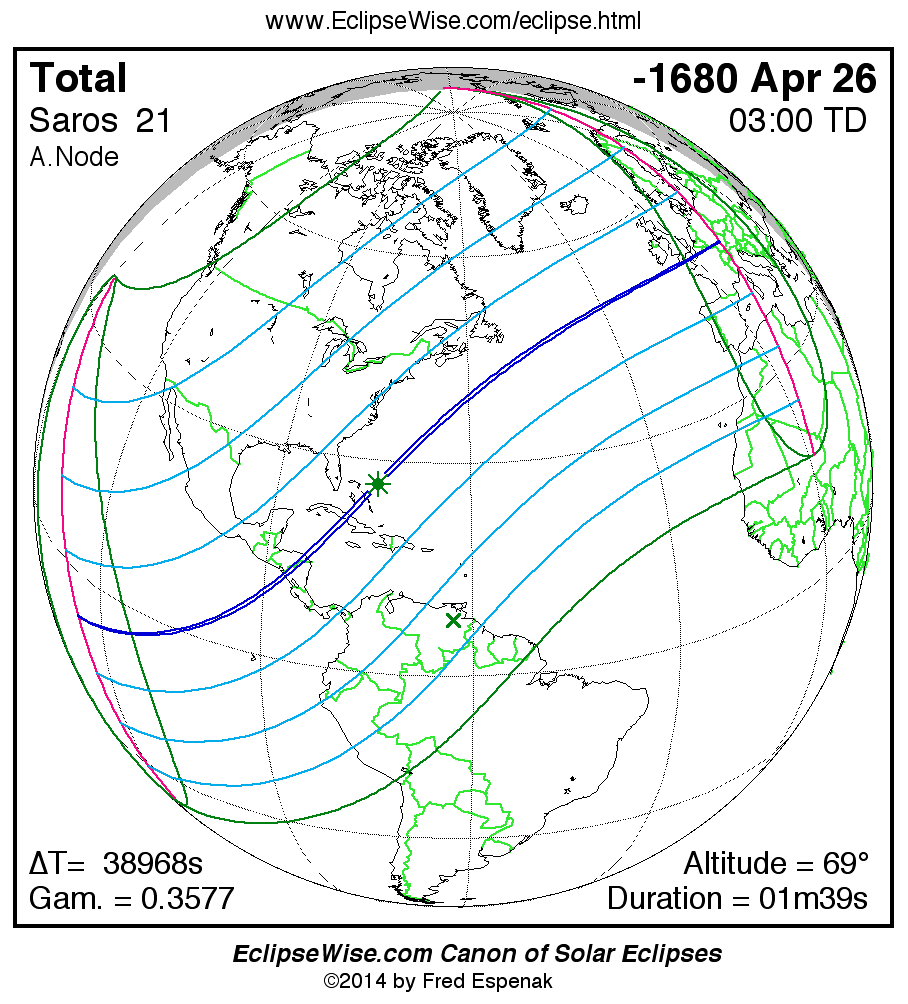
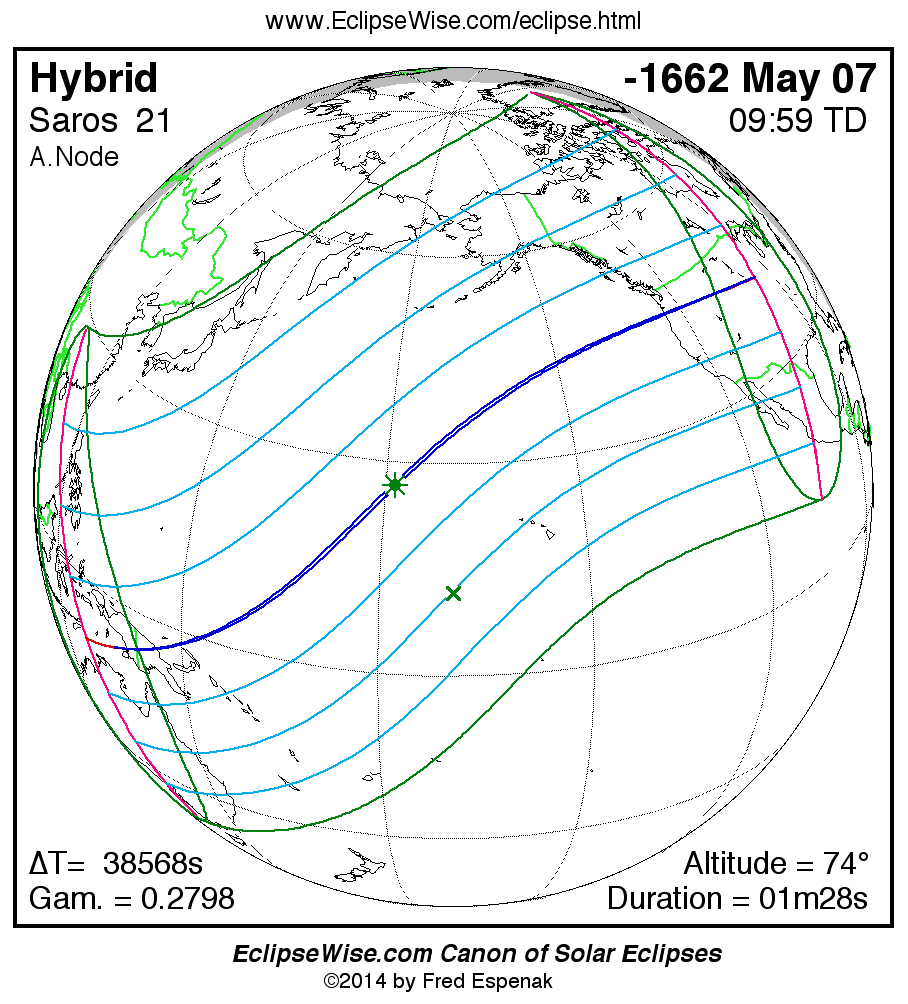
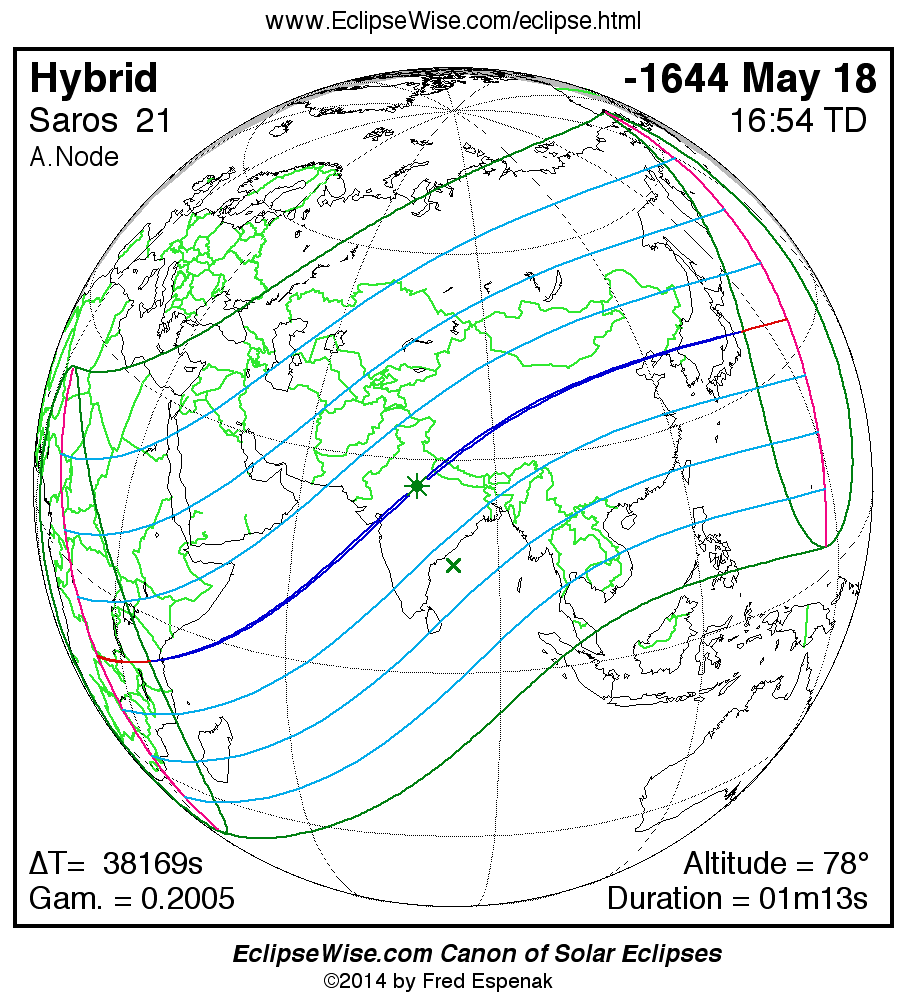
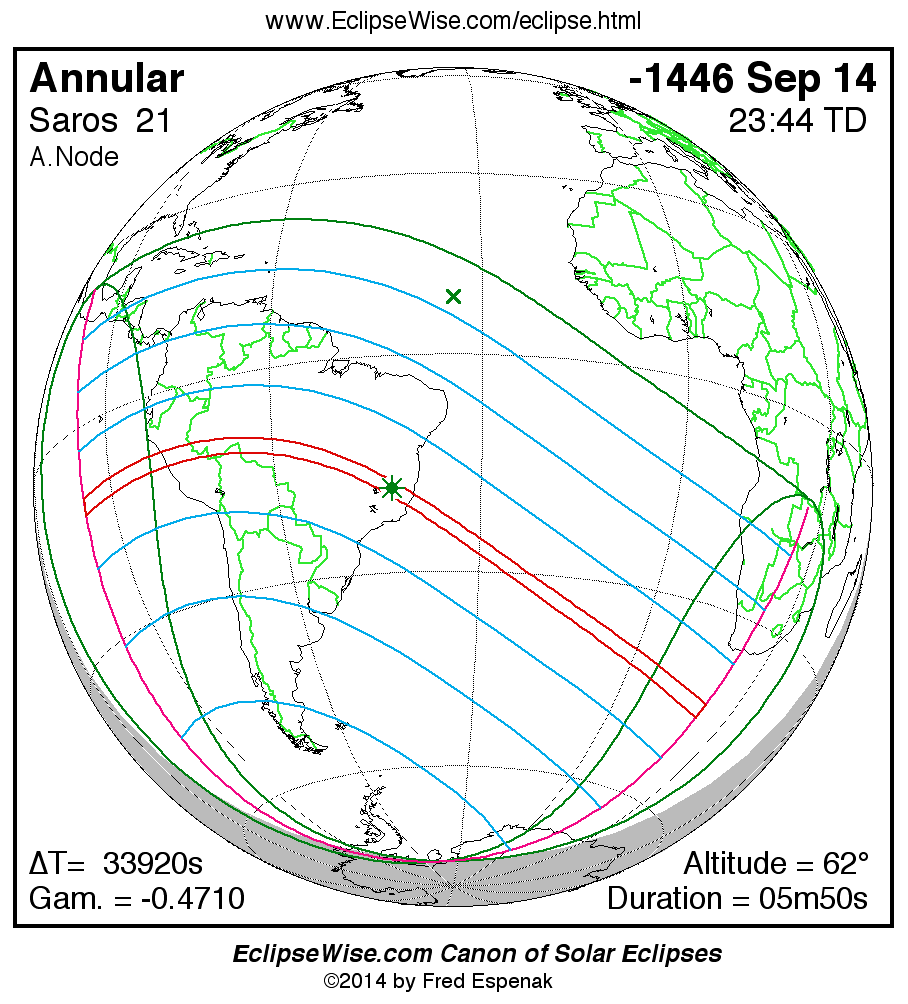
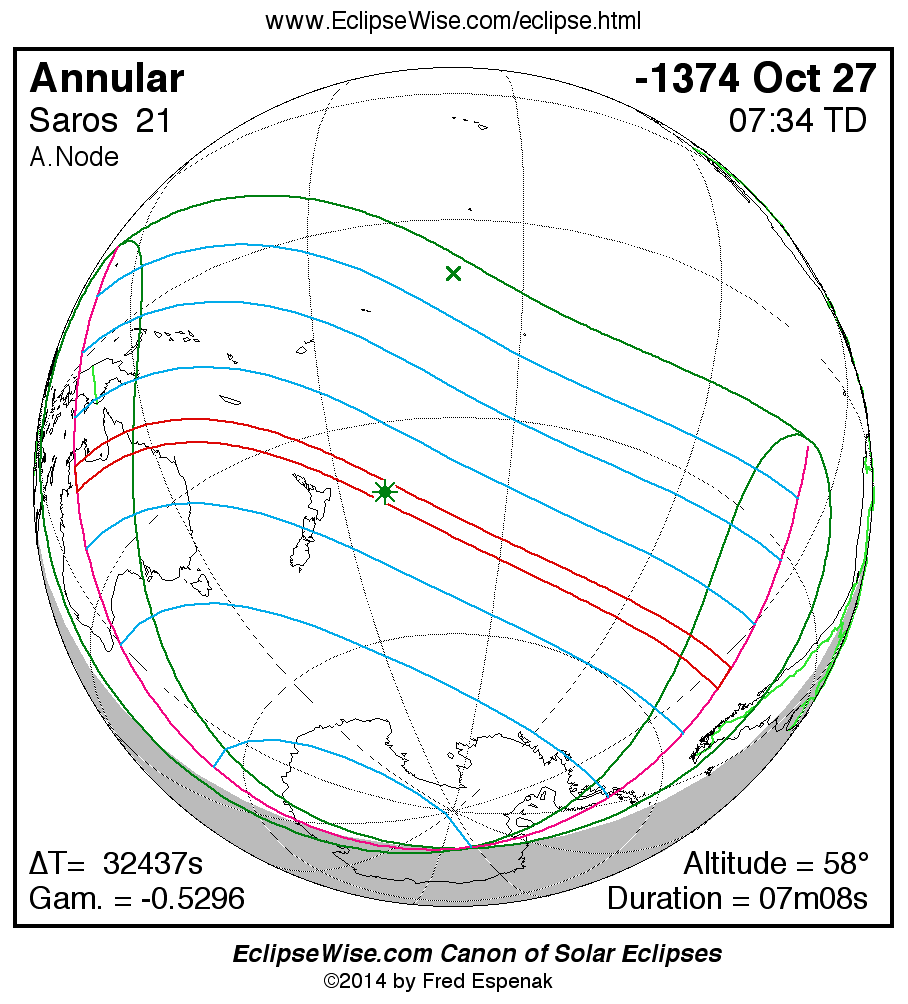
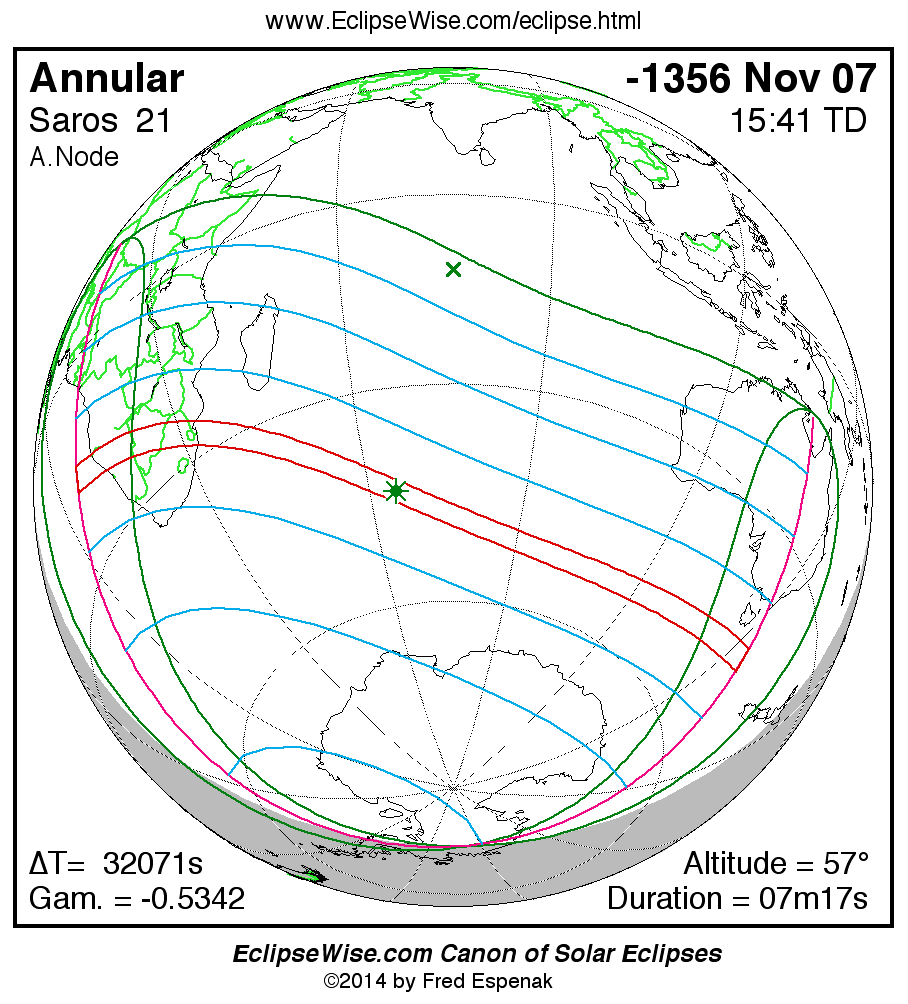
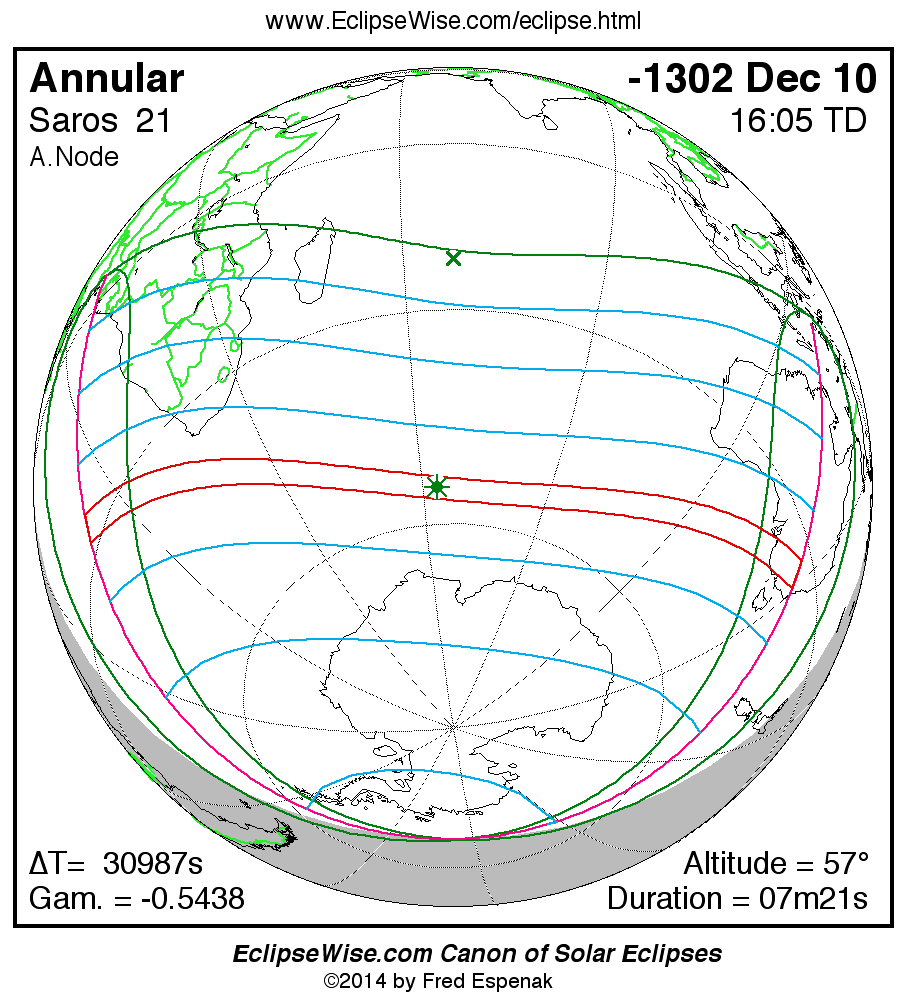
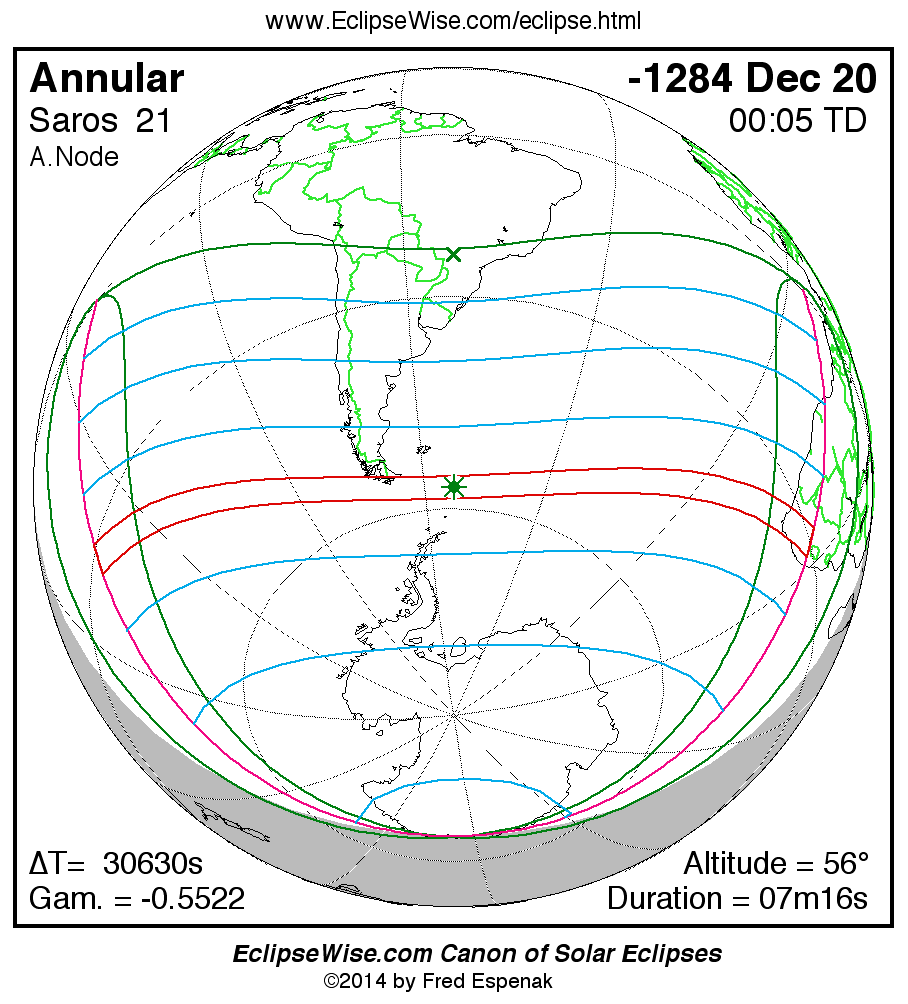
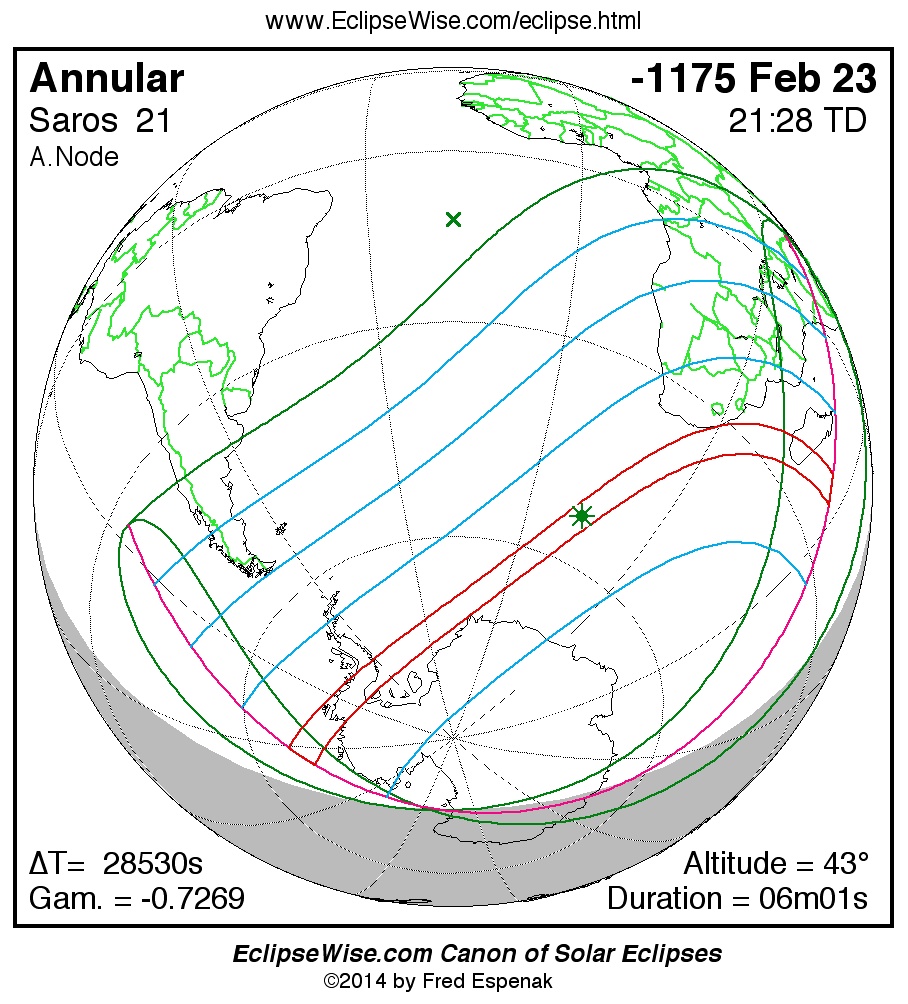
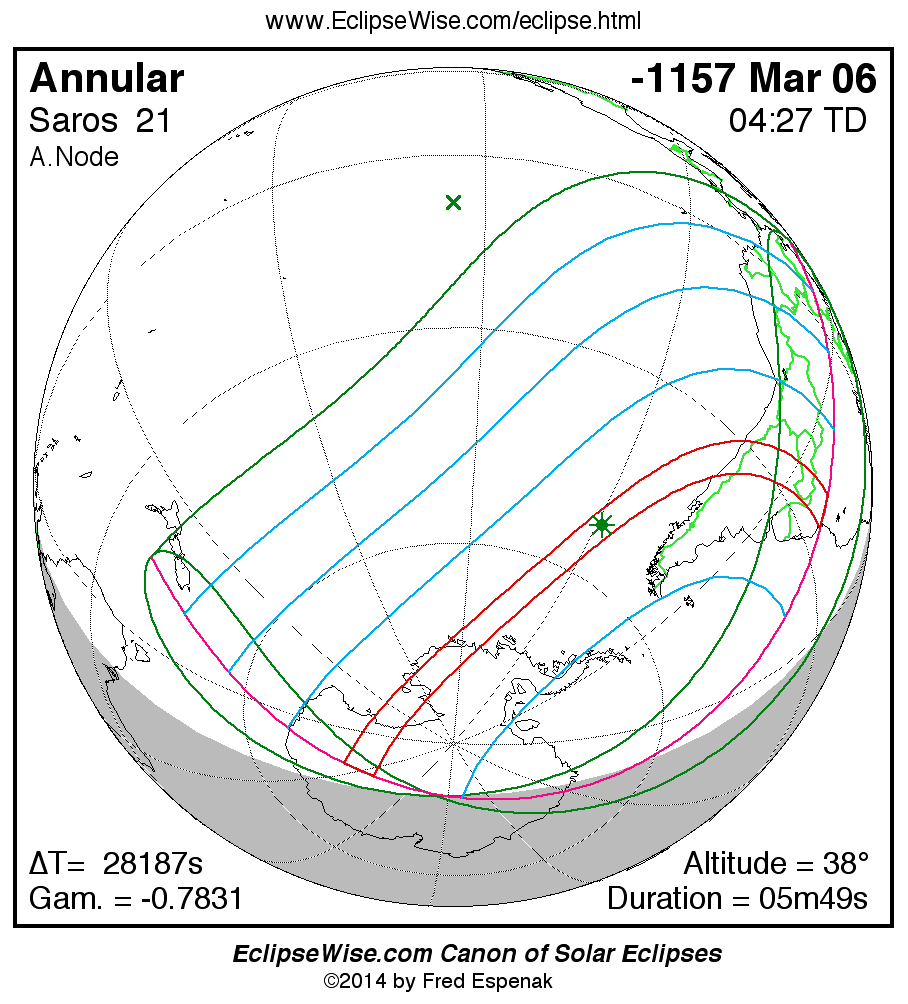
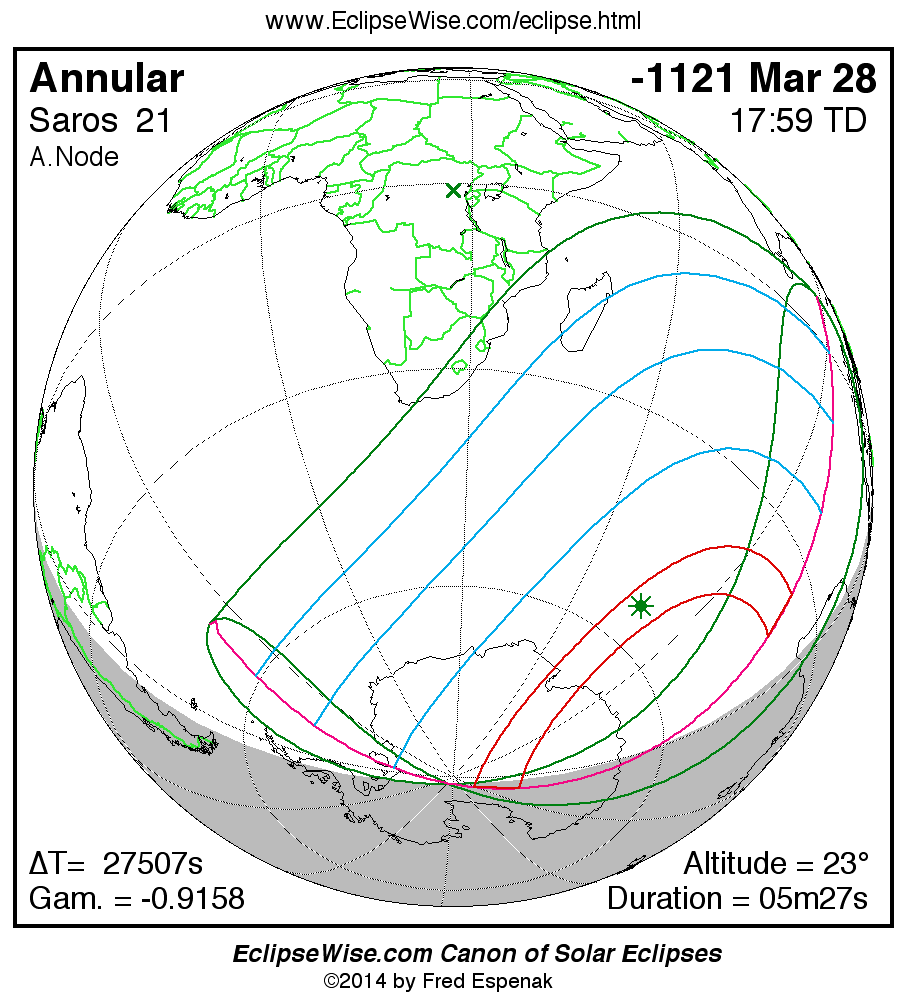
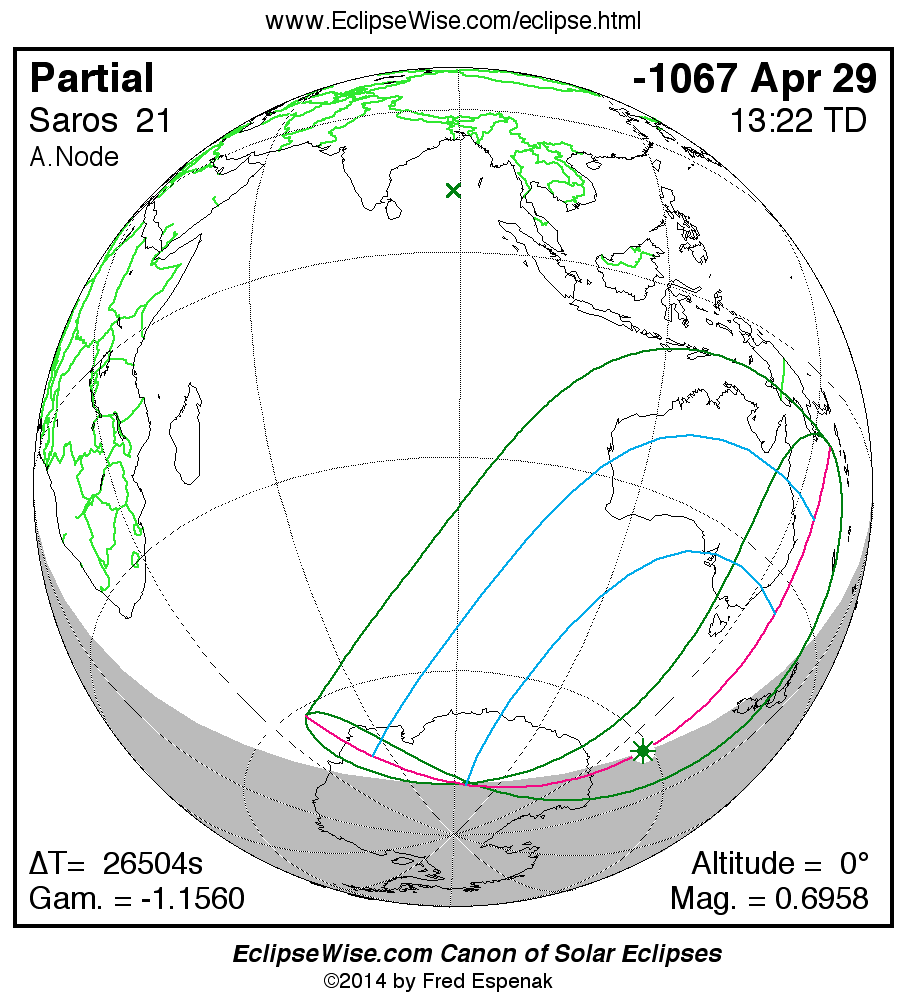
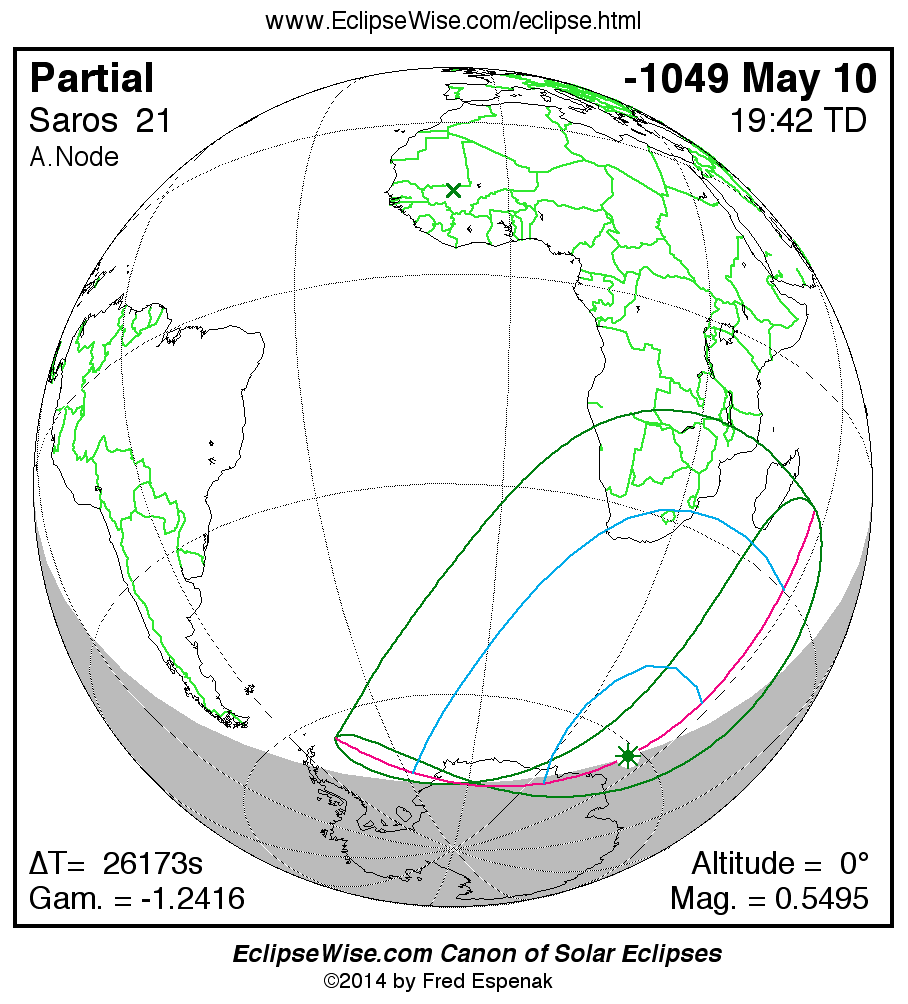
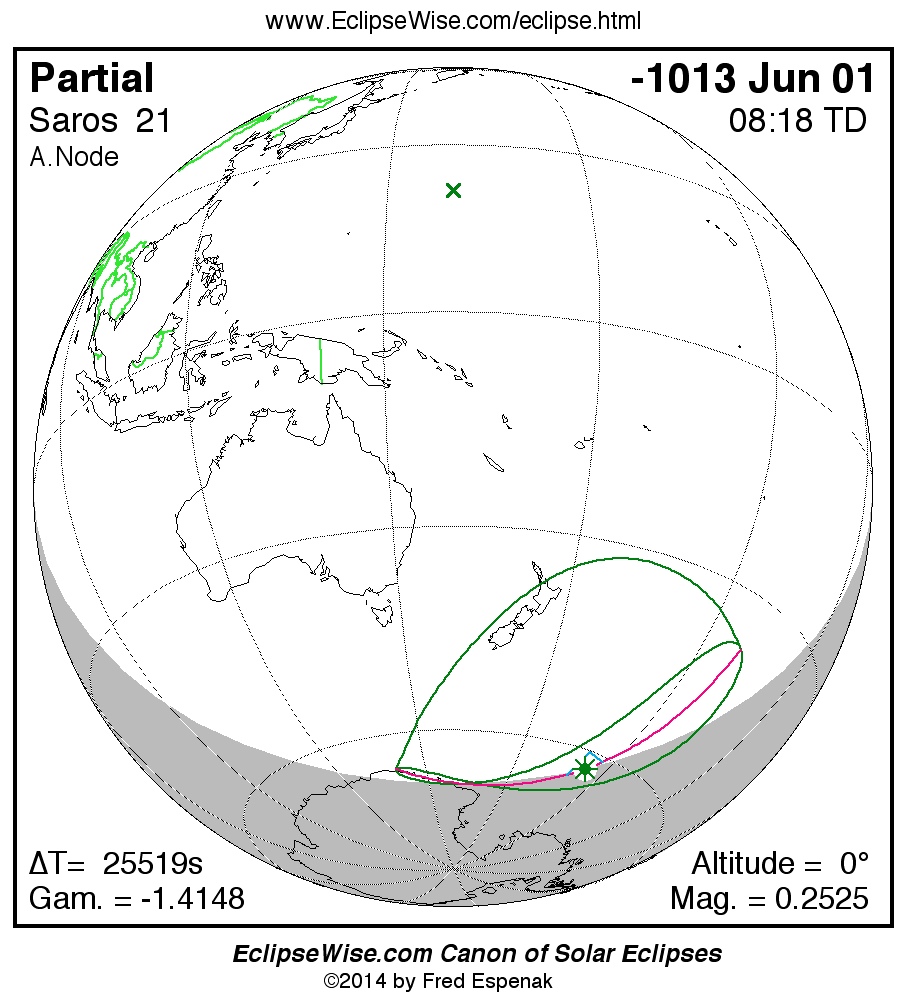
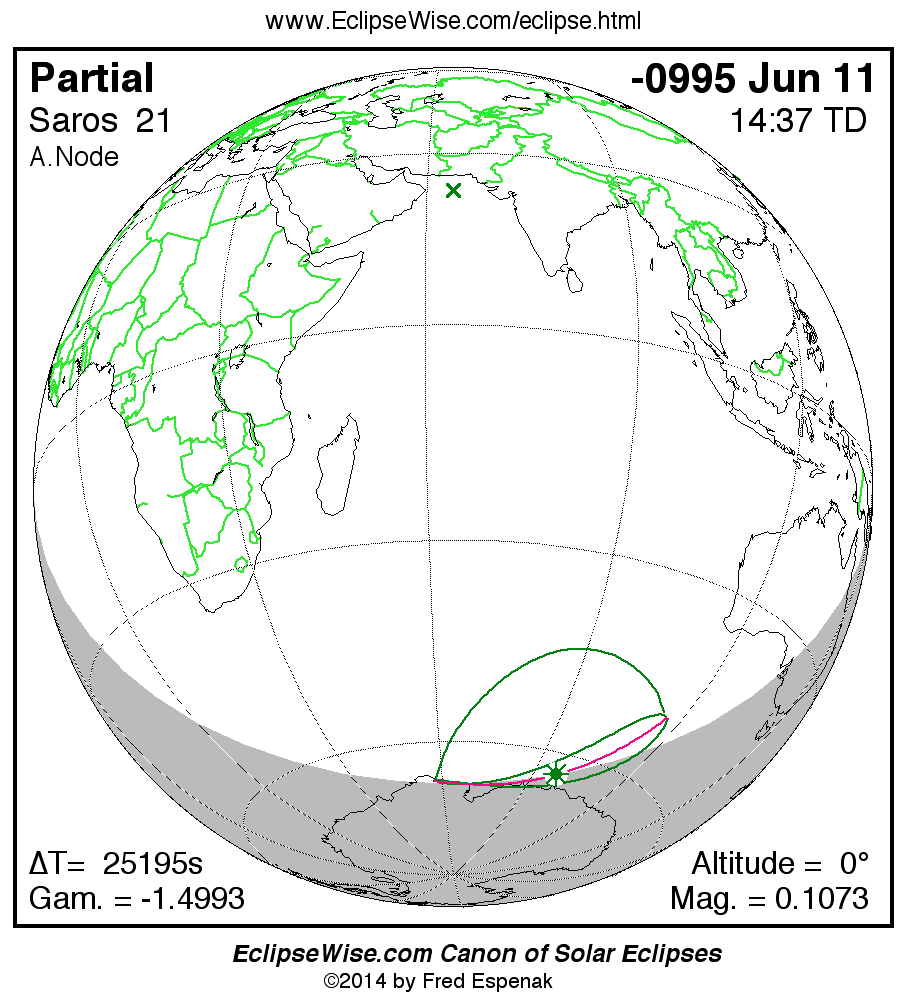
Saros 21
Panorama of Solar Eclipses of Saros 21
Fred Espenak
Introduction
A solar eclipse occurs whenever the Moon's shadow passes across Earth's surface. At least two solar eclipses and as many as five occur every year.
The periodicity and recurrence of solar eclipses is governed by the Saros cycle, a period of approximately 6,585.3 days (18 years 11 days 8 hours). When two eclipses are separated by a period of one Saros, they share a very similar geometry. The two eclipses occur at the same node with the Moon at nearly the same distance from Earth and the same time of year due to a harmonic in three cycles of the Moon's orbit. Thus, the Saros is useful for organizing eclipses into families or series. Each series typically lasts 12 to 13 centuries and contains 70 or more eclipses. Every saros series begins with a number of partial eclipses near one of Earth's polar regions. The series will then produce several dozen central eclipses before ending with a group of partial eclipses near the opposite pole. For more information, see Periodicity of Solar Eclipses.
Panorama of Solar Eclipses of Saros 21
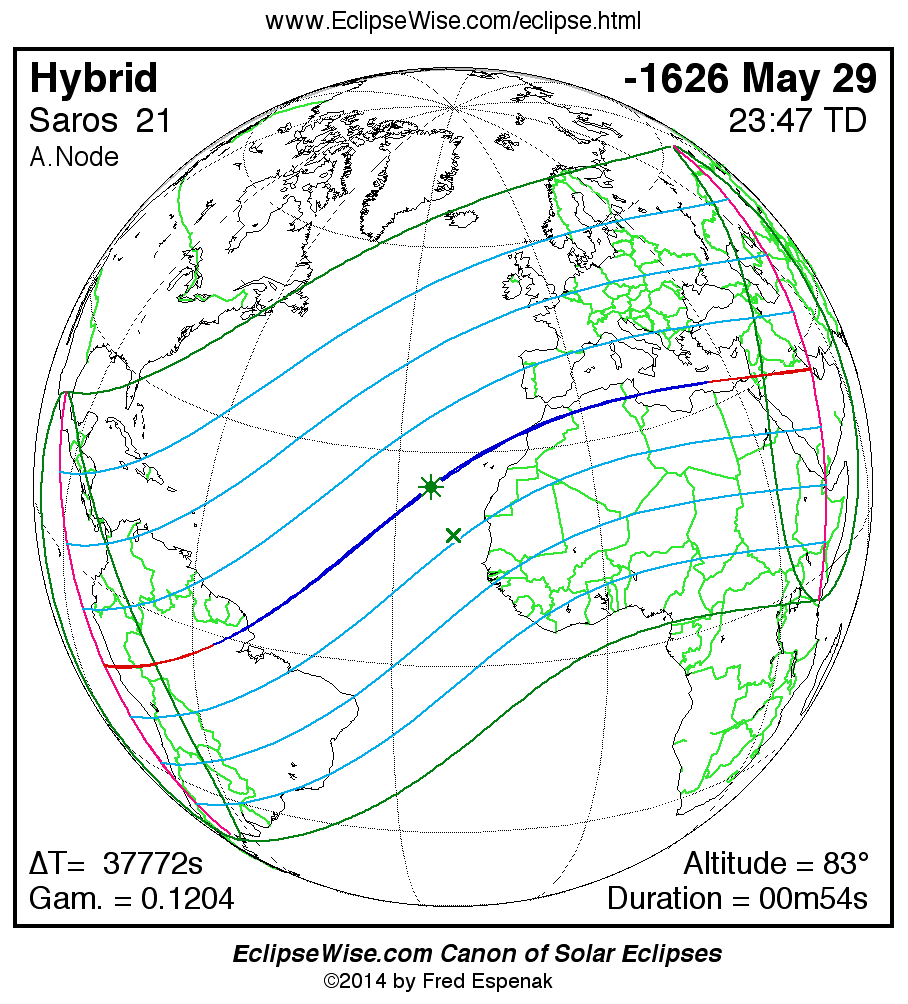
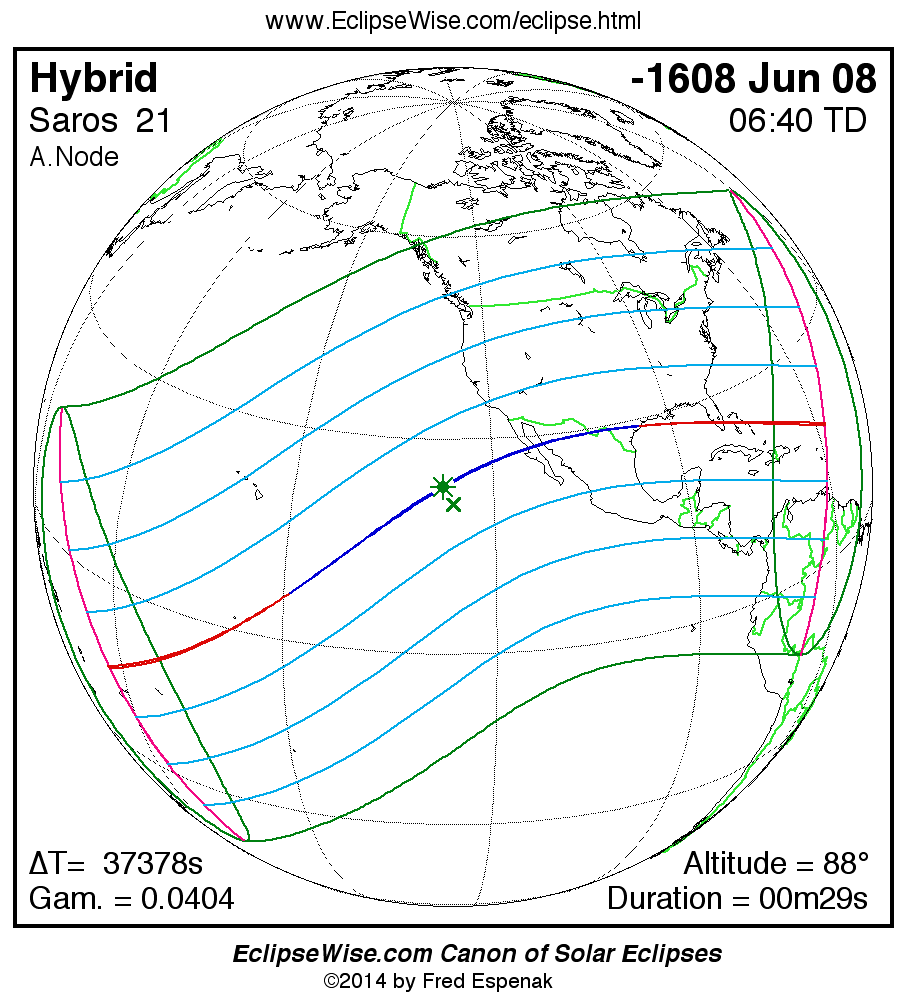
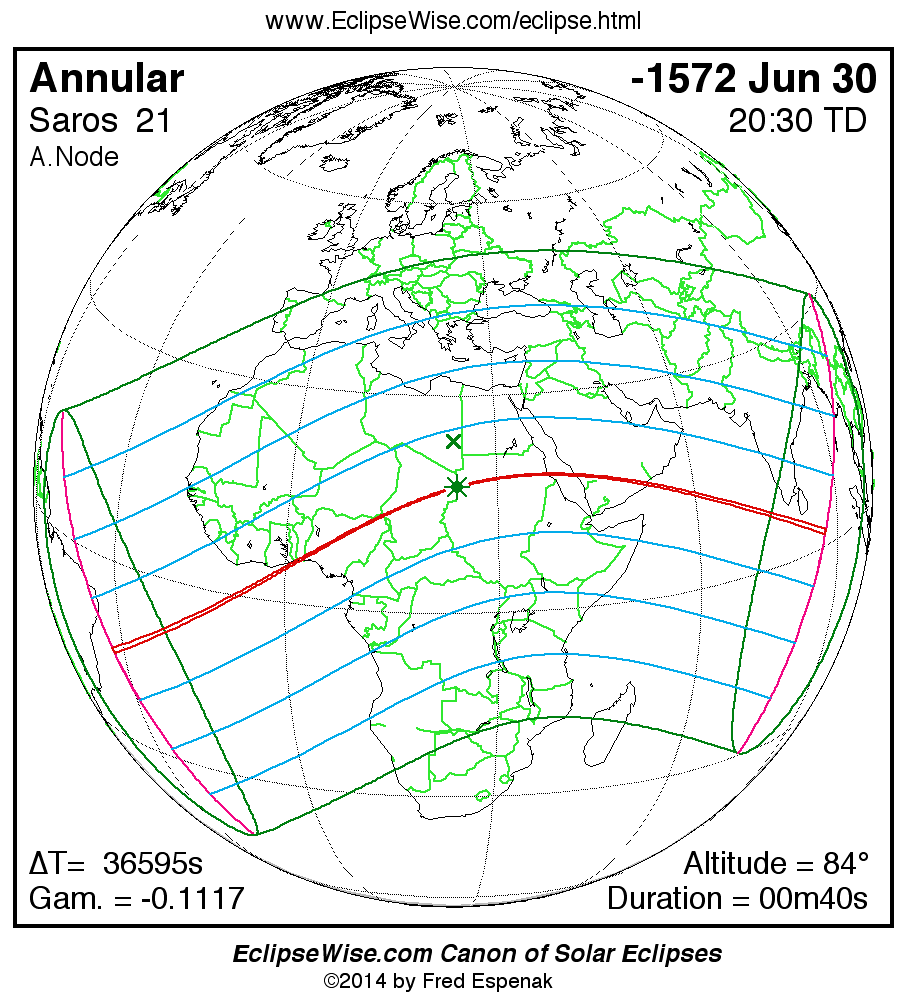
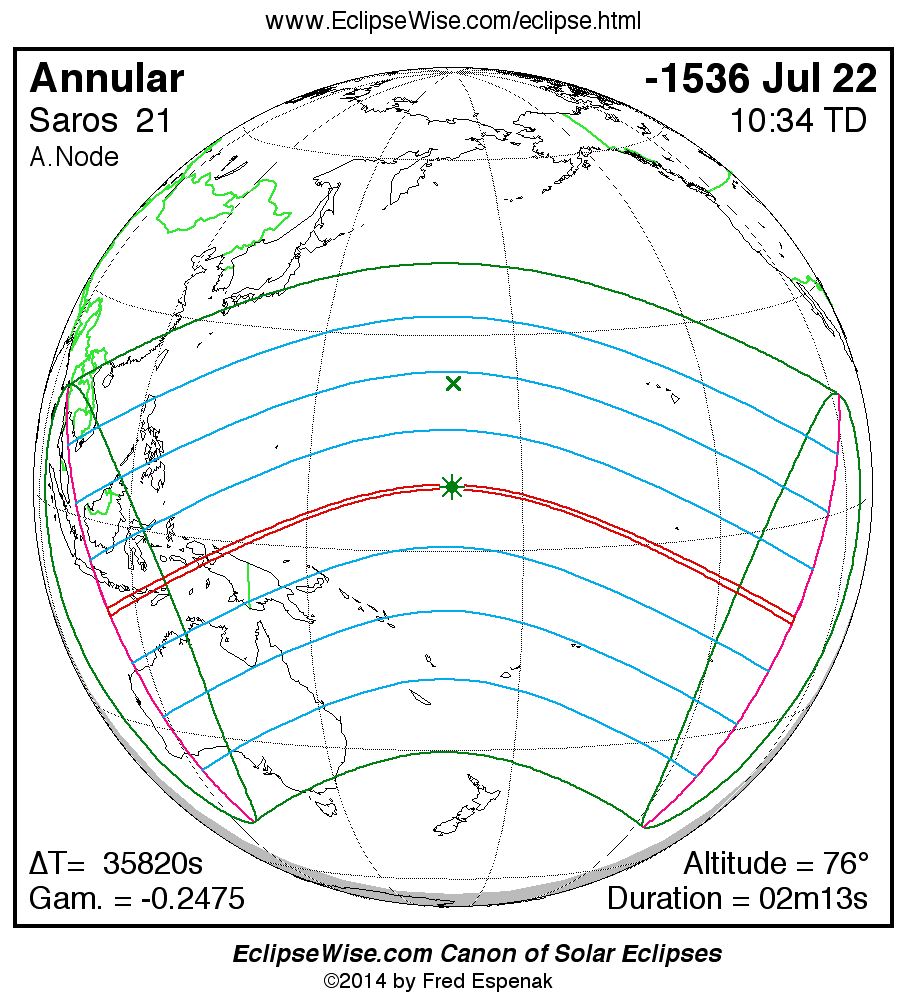
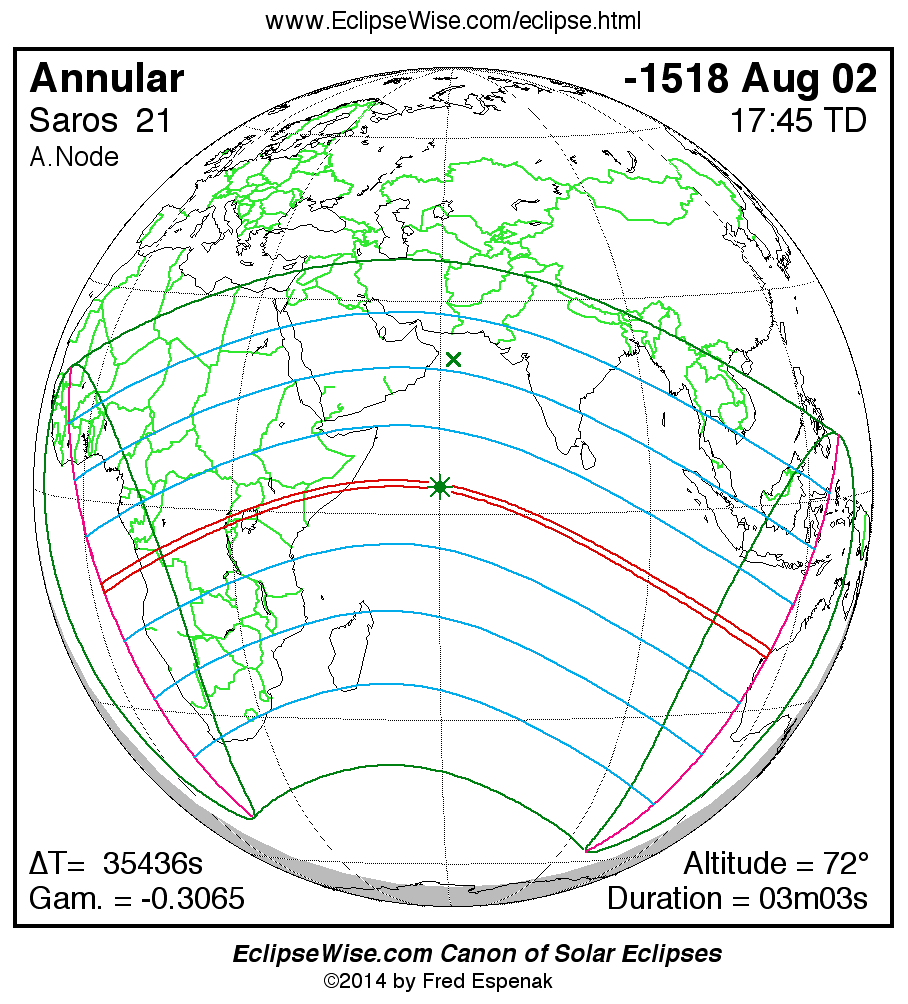
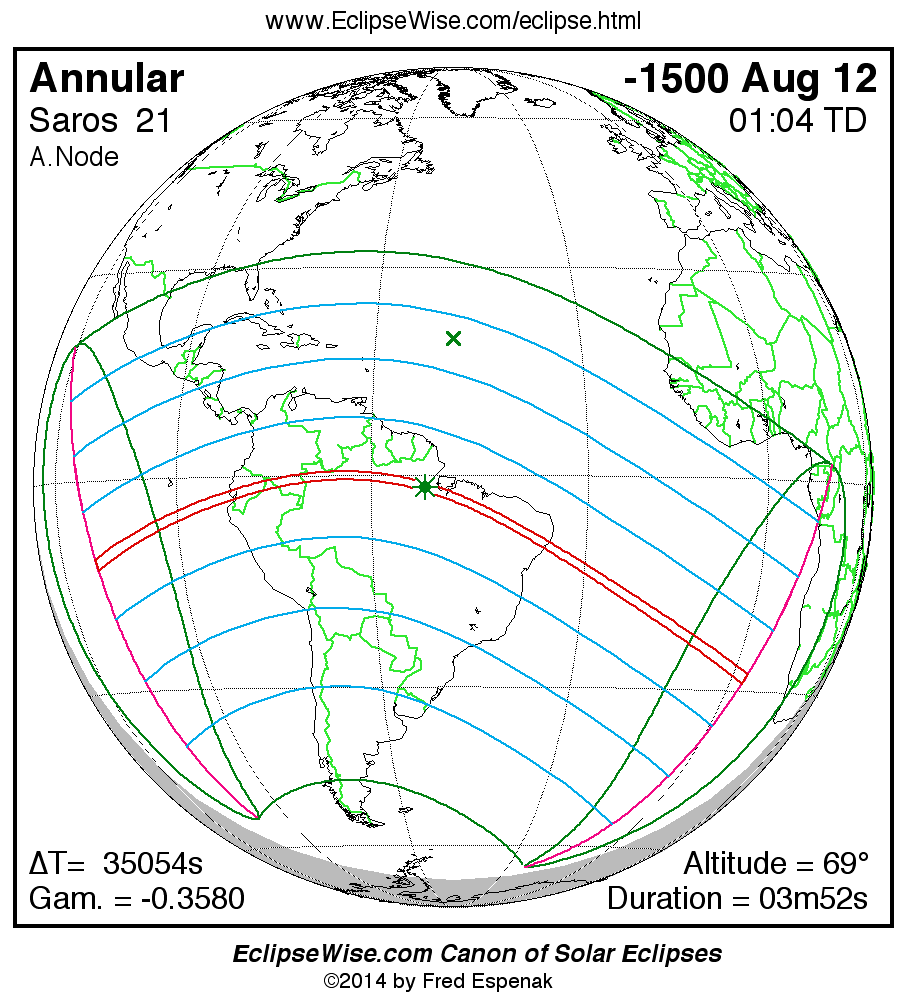
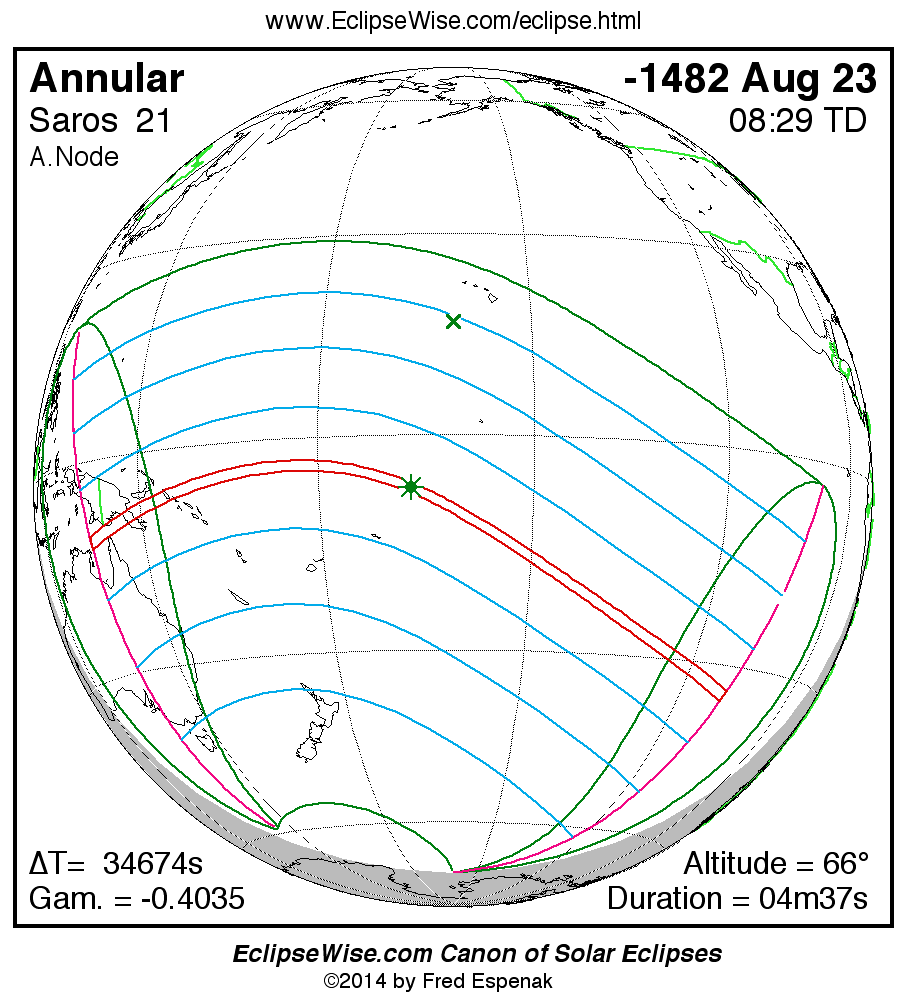
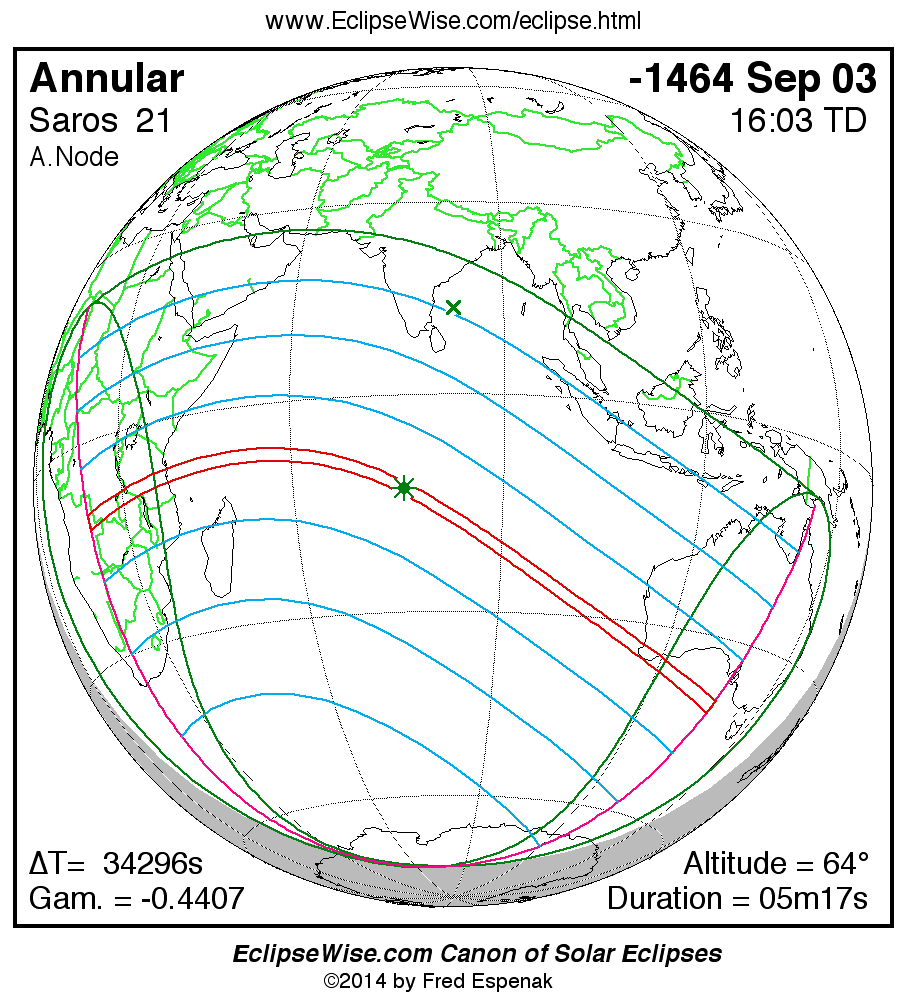
A panorama of all solar eclipses belonging to Saros 21 is presented here. Each map depicts the geographic region of visibility for a single eclipse. For central eclipses, the total or annular path is plotted in either blue (total) or red (annular). The date and time is given for the instant of Greatest Eclipse. Every map serves as a hyperlink to the EclipseWise Prime page for that eclipse where a larger map and complete details for the eclipse can be found. Visit the Key to Solar Eclipse Maps for a detailed explanation of these maps. Near the bottom of the page are a series of hyperlinks for more on solar eclipses.
The exeligmos is a period of three Saros cycles and is equal to approximately 54 years 33 days. Because it is nearly an integral number of days in length, two eclipses separated by 1 exeligmos (= 3 Saroses) not only share all the characterists of a Saros, but also take place in approximately the same geographic location.
The Saros panorama below is arranged in horizontal rows of 3 eclipses. So one eclipse to the left or right is a difference of 1 Saros cycle, and one eclipse above or below is a difference of 1 exeligmos. By scanning a column of the table, it reveals how the geographic visibility of eclipses separated by an exeligmos slowly changes.
- Click on any global map to go directly to the EclipseWise Prime Page for more information, tables, diagrams and maps. Key to Solar Eclipse Maps explains the features in these maps.
- Beneath each global eclipse map is a link Google Eclipse Map, that takes you to an interactive Google Map with the eclipse path plotted.
For more information on this series see Statistics for Solar Eclipses of Saros 21 .
Statistics for Solar Eclipses of Saros 21
Solar eclipses of Saros 21 all occur at the Moon’s ascending node and the Moon moves southward with each eclipse. The series began with a partial eclipse in the northern hemisphere on -2275 May 05. The series ended with a partial eclipse in the southern hemisphere on -0995 Jun 11. The total duration of Saros series 21 is 1280.14 years.
| Summary of Saros 21 | |
| First Eclipse | -2275 May 05 |
| Last Eclipse | -0995 Jun 11 |
| Series Duration | 1280.14 Years |
| No. of Eclipses | 72 |
| Sequence | 8P 26T 4H 28A 6P |
Saros 21 is composed of 72 solar eclipses as follows:
| Solar Eclipses of Saros 21 | |||
| Eclipse Type | Symbol | Number | Percent |
| All Eclipses | - | 72 | 100.0% |
| Partial | P | 14 | 19.4% |
| Annular | A | 28 | 38.9% |
| Total | T | 26 | 36.1% |
| Hybrid | H | 4 | 5.6% |
Umbral eclipses (annular, total and hybrid) can be further classified as either: 1) Central (two limits), 2) Central (one limit) or 3) Non-Central (one limit). The statistical distribution of these classes in Saros series 21 appears in the following table.
| Umbral Eclipses of Saros 21 | ||
| Classification | Number | Percent |
| All Umbral Eclipses | 58 | 100.0% |
| Central (two limits) | 56 | 96.6% |
| Central (one limit) | 1 | 1.7% |
| Non-Central (one limit) | 1 | 1.7% |
The 72 eclipses in Saros 21 occur in the following order : 8P 26T 4H 28A 6P
The longest and shortest central eclipses of Saros 21 as well as largest and smallest partial eclipses appear below.
| Extreme Durations and Magnitudes of Solar Eclipses of Saros 21 | |||
| Extrema Type | Date | Duration | Magnitude |
| Longest Annular Solar Eclipse | -1320 Nov 29 | 07m23s | - |
| Shortest Annular Solar Eclipse | -1590 Jun 20 | 00m02s | - |
| Longest Total Solar Eclipse | -2095 Aug 21 | 02m35s | - |
| Shortest Total Solar Eclipse | -1897 Dec 19 | 01m35s | - |
| Longest Hybrid Solar Eclipse | -1662 May 08 | 01m28s | - |
| Shortest Hybrid Solar Eclipse | -1608 Jun 09 | 00m29s | - |
| Largest Partial Solar Eclipse | -2149 Jul 20 | - | 0.92067 |
| Smallest Partial Solar Eclipse | -2275 May 05 | - | 0.01260 |
Links to Additional Solar Eclipse Predictions
- Home - home page of EclipseWise with predictions for both solar and lunar eclipses
- Solar Eclipses - primary page for solar eclipse predictions
- Solar Eclipse Links - detailed directory of links
- Solar Eclipse Basics - a primer on solar eclipses
- Catalog of Solar Eclipse Saros Series - covers Saros series -30 through 190
- Six Millennium Catalog of Solar Eclipses - from -2999 to +3000 (3000 BCE to 3000 CE)
- World Atlas of Solar Eclipse Maps - index page for world eclipse maps covering 5 millennia
- Javascript Solar Eclipse Explorer - calculate all solar eclipses visible from a city
- Thousand Year Canon of Solar Eclipses 1501 to 2500 - link to the publication
- MrEclipse.com - eclipse resources and tips on photography
- Solar Eclipses for Beginners - a primer on solar eclipse basics
- How to Photograph a Solar Eclipse - instructions for imaging an eclipse of the Sun
- MrEclipse Photo Index - an index of solar eclipse photographs
Calendar
The Gregorian calendar (also called the Western calendar) is internationally the most widely used civil calendar. It is named for Pope Gregory XIII, who introduced it in 1582. On this website, the Gregorian calendar is used for all calendar dates from 1582 Oct 15 onwards. Before that date, the Julian calendar is used. For more information on this topic, see Calendar Dates.
The Julian calendar does not include the year 0. Thus the year 1 BCE is followed by the year 1 CE (See: BCE/CE Dating Conventions). This is awkward for arithmetic calculations. Years in this catalog are numbered astronomically and include the year 0. Historians should note there is a difference of one year between astronomical dates and BCE dates. Thus, the astronomical year 0 corresponds to 1 BCE, and astronomical year -1 corresponds to 2 BCE, etc..
Eclipse Predictions
The eclipse predictions presented here were generated using the JPL DE406 solar and lunar ephemerides. The lunar coordinates have been calculated with respect to the Moon's Center of Mass.
The largest uncertainty in the eclipse predictions is caused by fluctuations in Earth's rotation due primarily to tidal friction of the Moon. The resultant drift in apparent clock time is expressed as ΔT and is determined as follows:
- pre-1950's: ΔT calculated from empirical fits to historical records derived by Morrison and Stephenson (2004)
- 1955-present: ΔT obtained from published observations
- future: ΔT is extrapolated from current values weighted by the long term trend from tidal effects
A series of polynomial expressions have been derived to simplify the evaluation of ΔT for any time from -2999 to +3000. The uncertainty in ΔT over this period can be estimated from scatter in the measurements.
Acknowledgments
Some of the content on this web site is based on the books Five Millennium Canon of Solar Eclipses: -1999 to +3000 and Thousand Year Canon of Solar Eclipses 1501 to 2500. All eclipse calculations are by Fred Espenak, and he assumes full responsibility for their accuracy.
Permission is granted to reproduce eclipse data when accompanied by a link to this page and an acknowledgment:
"Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, www.EclipseWise.com"
The use of diagrams and maps is permitted provided that they are NOT altered (except for re-sizing) and the embedded credit line is NOT removed or covered.